New 2025 Amazon ECS Managed Instance Support
Posted on January 17, 2026 • 8 minutes • 1663 words
sources:
- https://aws.amazon.com/tw/about-aws/whats-new/2025/09/amazon-ecs-managed-instances/
- https://aws.amazon.com/tw/about-aws/whats-new/2025/12/amazon-ecs-managed-instances-ec2-spot-instances/
Fast Nginx Task Startup with ECS Managed Instances
使用 ECS Managed Instances 快速啟動 Nginx 任務
This project demonstrates how to use Amazon ECS Managed Instances with Terraform to quickly bring up an ECS service running Nginx. 本專案展示如何使用 Terraform 搭配 Amazon ECS Managed Instances 快速啟動運行 Nginx 的 ECS 服務。
We also measure how long it takes from requesting a single task to the moment the application starts logging — roughly 40 seconds end-to-end. 我們也測量了從請求單一任務到應用程式開始記錄日誌所需的時間 — 端到端大約 40 秒。
-
Why ECS Managed Instances are interesting and useful
-
為什麼 ECS Managed Instances 值得關注且實用
-
What this Terraform example is doing at a high level
-
這個 Terraform 範例在高層次上做了什麼
-
Measured time from “no instances” to “first task running Nginx”
-
測量從「無實例」到「第一個 Nginx 任務運行」的時間
Why Care About ECS Managed Instances?
為什麼要關心 ECS Managed Instances?
When running workloads (tasks / services) on ECS, we typically think in terms of two classic options: 當在 ECS 上運行工作負載(任務/服務)時,我們通常會想到兩種經典選項:
-
ECS on EC2: You manage Auto Scaling Groups, lifecycle, capacity, patching, etc.
-
ECS on EC2:您需要自行管理 Auto Scaling Groups、生命週期、容量、修補程式等。
-
ECS on Fargate: No EC2 management, but higher per-unit cost and some limitations on supported sizes.
-
ECS on Fargate:無需管理 EC2,但單位成本較高且支援的規格有一些限制。
ECS Managed Instances sit somewhere in between: ECS Managed Instances 介於兩者之間:
-
You still use EC2 instances (so you can leverage Graviton, Spot, flexible instance families, etc.).
-
您仍然使用 EC2 實例(因此可以利用 Graviton、Spot、彈性實例系列等)。
-
But you don’t manage ASGs yourself. ECS uses a capacity provider to manage the EC2 instances for you — essentially “auto-managed EC2 capacity powered by ECS”.
-
但您不需要自己管理 ASG。ECS 使用容量提供者為您管理 EC2 實例 — 本質上是「由 ECS 驅動的自動管理 EC2 容量」。
For SREs/platform teams, this means: 對於 SRE/平台團隊來說,這意味著:
-
You define a pool of instances by attributes (instance requirements), e.g. ARM architecture, 2 vCPUs, 4–6 GB memory, etc.
-
您可以透過屬性(實例需求)定義一組實例池,例如 ARM 架構、2 個 vCPU、4-6 GB 記憶體等。
-
You don’t maintain ASGs and scaling policies directly; instead, you use an ECS capacity provider strategy to select capacity sources.
-
您不需要直接維護 ASG 和擴展策略;相反,您使用 ECS 容量提供者策略來選擇容量來源。
-
With CloudWatch Logs and Container Insights, the operational experience is close to Fargate, but the cost and flexibility look much more like EC2.
-
透過 CloudWatch Logs 和 Container Insights,操作體驗接近 Fargate,但成本和彈性則更像 EC2。
Terraform Example: Architecture Overview
Terraform 範例:架構概述
Demo Repo: https://github.com :neilkuan/ecs-managed-instance-issue
git clone https://github.com:neilkuan/ecs-managed-instance-issue
The main.tf file wires everything together in ap-east-2. At a high level it does the following:
main.tf 檔案在 ap-east-2 區域將所有元件串接在一起。在高層次上,它執行以下操作:
-
Provider and Version Requirements
-
Provider 和版本需求
- Uses the
hashicorp/awsprovider, version>= 6.25.0, to support themanaged_instances_providerconfiguration. - 使用
hashicorp/awsprovider,版本>= 6.25.0,以支援managed_instances_provider設定。
- Uses the
-
Networking and Security Groups
-
網路和安全群組
-
Uses
data "aws_subnets"to fetch private subnets from an existing VPC. -
使用
data "aws_subnets"從現有 VPC 中取得私有子網路。 -
Creates two security groups:
-
建立兩個安全群組:
-
ecs_instances: for EC2 instances, allowing outbound traffic. -
ecs_instances:用於 EC2 實例,允許出站流量。 -
ecs_tasks: for ECS tasks, allowing inbound HTTP (port 80/tcp) so requests can reach Nginx. -
ecs_tasks:用於 ECS 任務,允許入站 HTTP(連接埠 80/tcp),以便請求可以到達 Nginx。
-
-
-
IAM Roles and Instance Profile
-
IAM 角色和實例設定檔
-
ecs_infrastructure_role: used by the ECS infrastructure (Managed Instances), attached with: -
ecs_infrastructure_role:由 ECS 基礎設施(Managed Instances)使用,附加:arn:aws:iam::aws:policy/AmazonECSInfrastructureRolePolicyForManagedInstances.arn:aws:iam::aws:policy/AmazonECSInfrastructureRolePolicyForManagedInstances。
-
ecs_instance_role: used by EC2 instances, attached with: -
ecs_instance_role:由 EC2 實例使用,附加:AmazonEC2ContainerServiceforEC2RoleAmazonEC2ContainerServiceforEC2Role
-
ecs_task_execution_role: ECS task execution role, attached with: -
ecs_task_execution_role:ECS 任務執行角色,附加:AmazonECSTaskExecutionRolePolicy(image pulls, logging, etc.).AmazonECSTaskExecutionRolePolicy(映像檔拉取、日誌記錄等)。
-
-
ECS Cluster and Capacity Provider
-
ECS 叢集和容量提供者
-
Creates an ECS cluster:
managed-instances-cluster. -
建立 ECS 叢集:
managed-instances-cluster。 -
Creates a capacity provider
managed-instances-cpusingmanaged_instances_provider: -
使用
managed_instances_provider建立容量提供者managed-instances-cp:-
Sets
infrastructure_role_arnandinstance_launch_template. -
設定
infrastructure_role_arn和instance_launch_template。 -
Uses
instance_requirementsto define the desired EC2 pool: -
使用
instance_requirements定義所需的 EC2 池:-
vCPU between 2–4, memory between 3–6 GiB.
-
vCPU 介於 2-4 之間,記憶體介於 3-6 GiB 之間。
-
cpu_manufacturers = ["amazon-web-services"]to prefer Graviton (e.g. t4g, c7g, m7g). -
cpu_manufacturers = ["amazon-web-services"]以優先使用 Graviton(例如 t4g、c7g、m7g)。 -
Excludes very small instance types (
t4g.nano,t4g.micro,t4g.small). -
排除非常小的實例類型(
t4g.nano、t4g.micro、t4g.small)。
-
-
Configures
network_configurationto use private subnets and theecs_instancessecurity group. -
設定
network_configuration以使用私有子網路和ecs_instances安全群組。 -
Defines
storage_configurationand setsmonitoring = "BASIC". -
定義
storage_configuration並設定monitoring = "BASIC"。
-
-
Uses
aws_ecs_cluster_capacity_providersto attach the capacity provider to the cluster and make it the default strategy. -
使用
aws_ecs_cluster_capacity_providers將容量提供者附加到叢集並將其設為預設策略。
-
-
Task Definition and Nginx Service
-
任務定義和 Nginx 服務
-
Task definition
nginx-task: -
任務定義
nginx-task:-
network_mode = "awsvpc"andrequires_compatibilities = ["EC2", "MANAGED_INSTANCES"]. -
network_mode = "awsvpc"且requires_compatibilities = ["EC2", "MANAGED_INSTANCES"]。 -
runtime_platformset toLINUXwithARM64to match Graviton instances. -
runtime_platform設定為LINUX搭配ARM64以匹配 Graviton 實例。 -
Container image:
public.ecr.aws/nginx/nginx:1.27-alpine-arm64v8, exposing port 80 and sending logs to CloudWatch Logs (/ecs/nginx-managed-instances) viaawslogs. -
容器映像檔:
public.ecr.aws/nginx/nginx:1.27-alpine-arm64v8,暴露連接埠 80 並透過awslogs將日誌傳送到 CloudWatch Logs(/ecs/nginx-managed-instances)。
-
-
ECS service
nginx-service: -
ECS 服務
nginx-service:-
desired_count = 1and acapacity_provider_strategypointing tomanaged-instances-cp. -
desired_count = 1且capacity_provider_strategy指向managed-instances-cp。 -
Uses the same private subnets and the
ecs_taskssecurity group. -
使用相同的私有子網路和
ecs_tasks安全群組。
-
-
In other words, with a single terraform apply you get:
換句話說,透過單一 terraform apply 您可以獲得:
-
An ECS cluster backed by ECS Managed Instances.
-
由 ECS Managed Instances 支撐的 ECS 叢集。
-
A service that triggers ECS to spin up EC2 capacity and then launch an Nginx task.
-
觸發 ECS 啟動 EC2 容量並執行 Nginx 任務的服務。
-
CloudWatch Logs and basic monitoring already wired in.
-
已預先設定好的 CloudWatch Logs 和基本監控。
Example Deploy Demo Infra
# init
terraform init
# apply
terraform apply
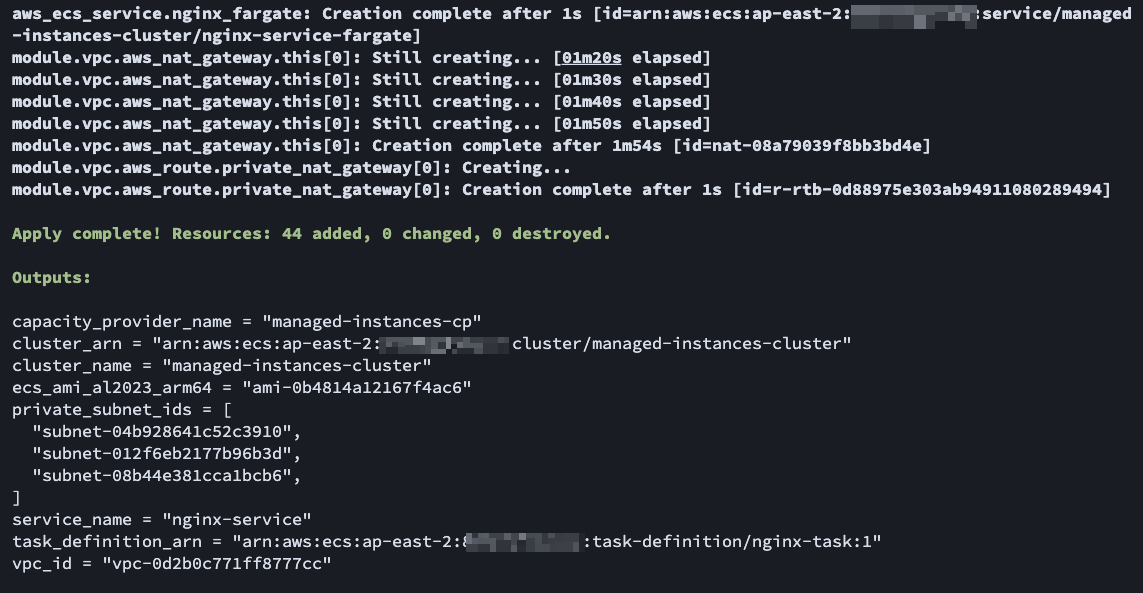
# Destroy
terraform destroy
Measuring Cold Start: From Requesting 1 Task to Nginx Logging
測量冷啟動:從請求 1 個任務到 Nginx 記錄日誌
To understand the cold-start behavior of Managed Instances, we used a small script that continuously lists container instances in the cluster. 為了了解 Managed Instances 的冷啟動行為,我們使用了一個小腳本持續列出叢集中的容器實例。
Monitoring Script
監控腳本
bash -c 'while true; do date && aws ecs list-container-instances --cluster managed-instances-cluster;done'
This prints the current time and the result of aws ecs list-container-instances every second so we can see:
這會每秒列印當前時間和 aws ecs list-container-instances 的結果,讓我們可以看到:
-
When there are no EC2 instances registered to the cluster.
-
叢集中何時沒有已註冊的 EC2 實例。
-
When the first managed instance appears and registers with ECS.
-
第一個受管實例何時出現並註冊到 ECS。
Timeline and Results
時間線和結果
Here’s the timeline from “requesting 1 Nginx task” to “Nginx starting to write logs”: 以下是從「請求 1 個 Nginx 任務」到「Nginx 開始寫入日誌」的時間線:
17:04:46 request 1 task
-> (19s)
17:05:5 container instance running (c6g.large)
-> (15s) (pending) -> (running)
17:05:20 task running
-> (7s)
17:05:27 application (nginx) logging
Interpreted step-by-step: 逐步解讀:
-
0s: Request to start one Nginx task on
managed-instances-cluster. -
0 秒:請求在
managed-instances-cluster上啟動一個 Nginx 任務。 -
-
-
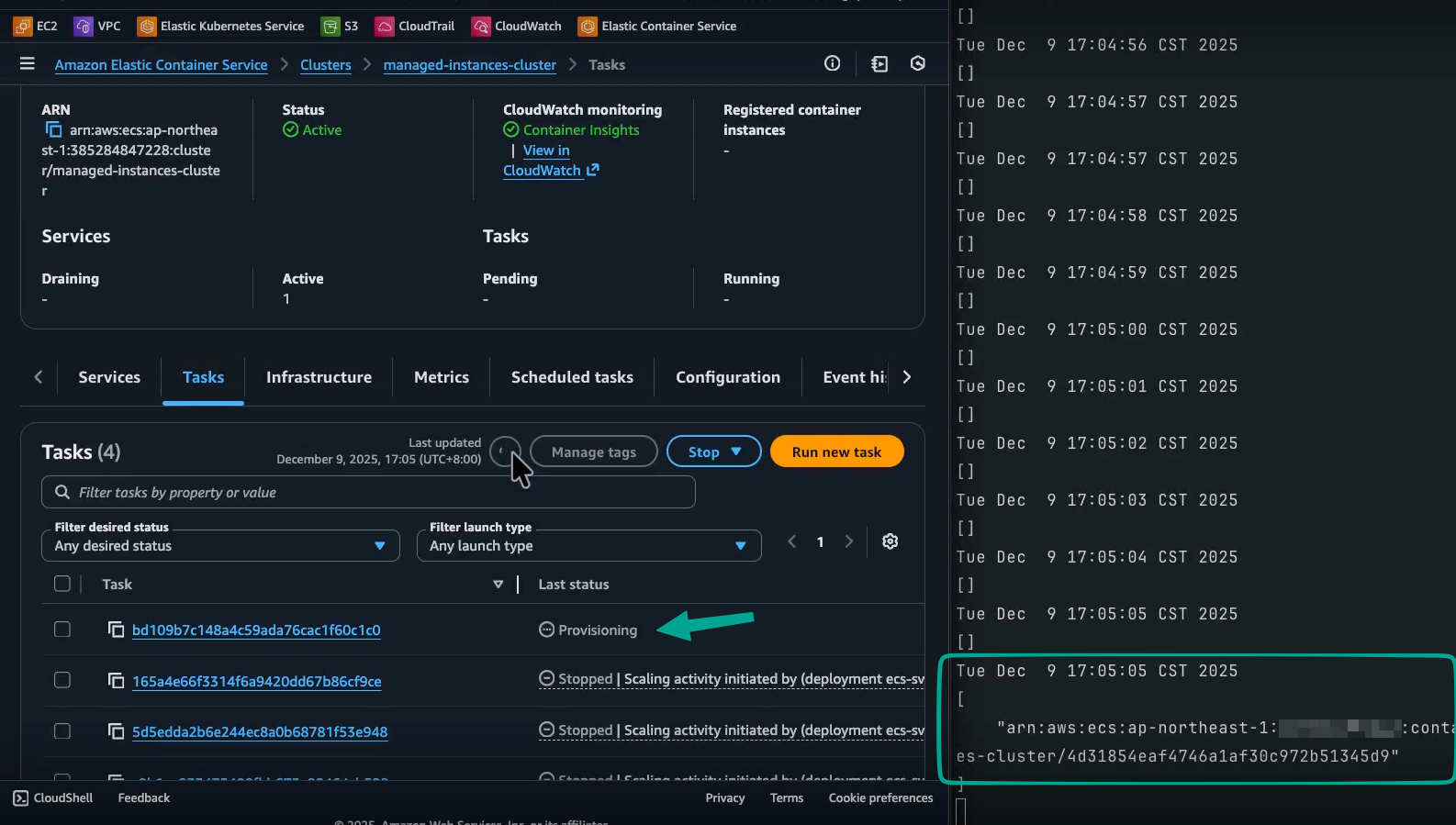
~19s later: The first managed instance (in this run,
c6g.large) is launched and registered to the ECS cluster. -
約 19 秒後:第一個受管實例(此次執行為
c6g.large)啟動並註冊到 ECS 叢集。 -
-
~15s after that: The ECS task reaches
RUNNINGstate. -
之後約 15 秒:ECS 任務達到
RUNNING狀態。 -
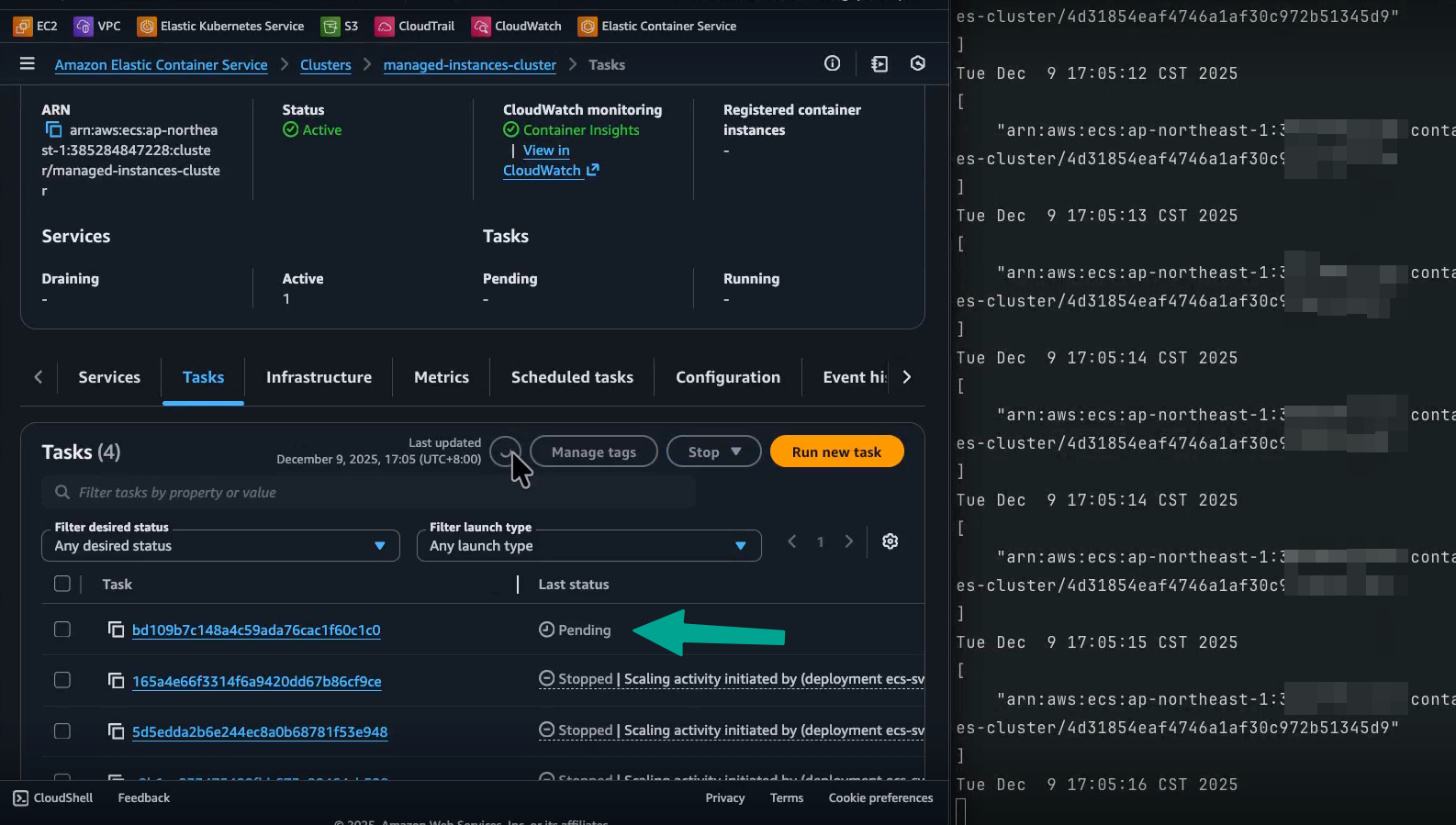
-
~7s later: Nginx starts writing application logs to CloudWatch Logs.
-
再過約 7 秒:Nginx 開始將應用程式日誌寫入 CloudWatch Logs。
-
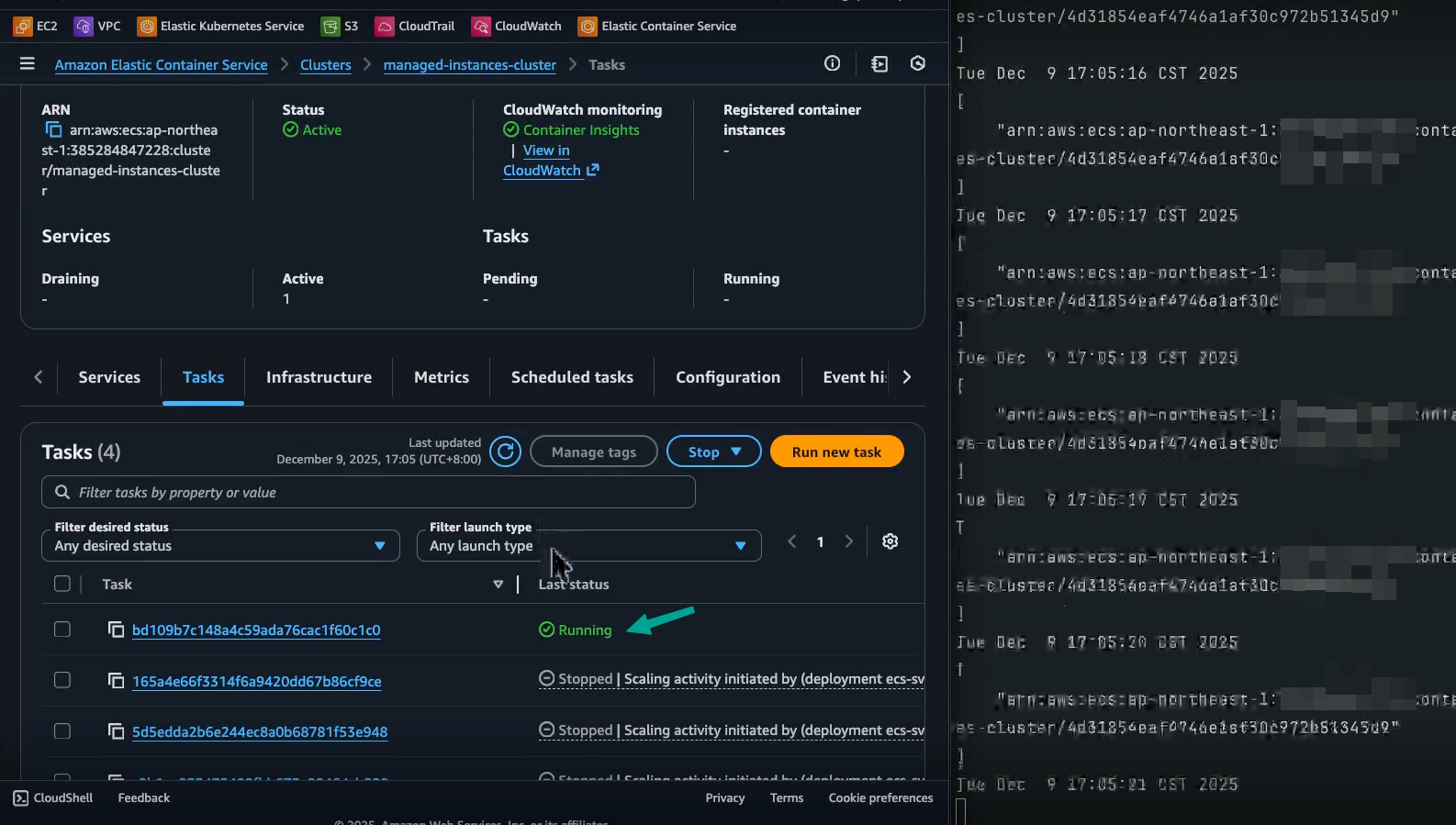
-
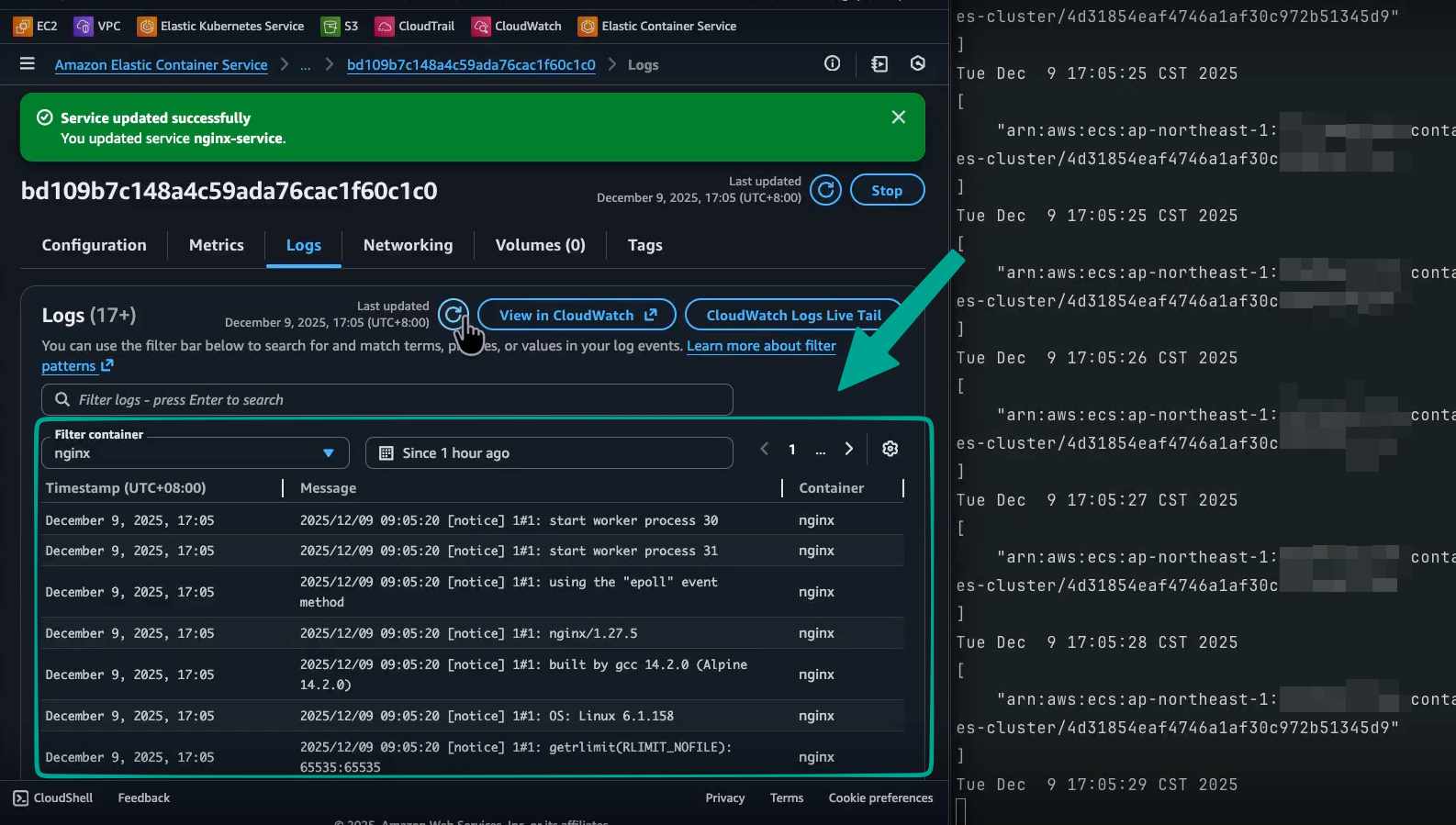
So, from “no container instances at all” to “Nginx actually serving and logging” you’re looking at roughly: 因此,從「完全沒有容器實例」到「Nginx 實際服務並記錄日誌」大約需要:
19s (bring up EC2 + register) + 15s (pull image & start container) + 7s (app startup & first logs) ≒ 41 seconds 19 秒(啟動 EC2 + 註冊)+ 15 秒(拉取映像檔 & 啟動容器)+ 7 秒(應用程式啟動 & 首次日誌)≒ 41 秒
For many back-office services, internal tools, or low-QPS control-plane style workloads: 對於許多後台服務、內部工具或低 QPS 控制平面類型的工作負載:
-
This cold-start time is perfectly reasonable.
-
這個冷啟動時間完全合理。
-
You still gain the cost benefits and flexibility of EC2/Graviton.
-
您仍然可以獲得 EC2/Graviton 的成本優勢和彈性。
When to Consider ECS Managed Instances
何時考慮使用 ECS Managed Instances
Some scenarios where ECS Managed Instances can be a great fit: 以下是 ECS Managed Instances 非常適合的一些場景:
-
You want EC2 flexibility and cost-efficiency without maintaining ASGs yourself.
-
您想要 EC2 的彈性和成本效益,但不想自己維護 ASG。
-
Your workloads are bursty or intermittent, and you’re okay with tens of seconds of cold start to avoid paying for idle EC2 capacity.
-
您的工作負載具有突發性或間歇性,您可以接受數十秒的冷啟動時間,以避免為閒置的 EC2 容量付費。
-
You need specific instance attributes (e.g. must run on Graviton, must have local NVMe, or must leverage Spot), but still want to orchestrate everything using ECS capacity provider strategies.
-
您需要特定的實例屬性(例如必須在 Graviton 上運行、必須有本地 NVMe、或必須利用 Spot),但仍希望使用 ECS 容量提供者策略來編排一切。
If you’re already familiar with ECS on EC2 or Fargate and want a more hands-off way of managing EC2 capacity, this ecs-mg example is a good starting point.
如果您已經熟悉 ECS on EC2 或 Fargate,並且想要一種更省事的 EC2 容量管理方式,這個 ecs-mg 範例是一個很好的起點。
Just run terraform apply, watch the cluster come to life, and observe how Managed Instances handle capacity and cold starts for your Nginx service.
只需執行 terraform apply,觀察叢集啟動,並觀察 Managed Instances 如何為您的 Nginx 服務處理容量和冷啟動。
Findings / 發現一些事情
1. ECS Service Connect with ECS Exec on Managed Instance has connection issues
1. 當 ECS Service Connect 與 ECS Exec 同時啟用時,Managed Instance 上的 Task 無法正常連線
If you deploy this Terraform example repo, the
nginx-servicewill enable both ECS Service Connect and ECS Exec running on Managed Instance.如果你部署了這個 Terraform 範例,
nginx-service會同時開啟 ECS Service Connect 以及 ECS Exec,並運行於 Managed Instance 上。
Example / 範例:
aws ecs list-services --cluster managed-instances-cluster --region ap-east-2 --query 'serviceArns[]' --output table
# ------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
# | ListServices |
# +----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------+
# | arn:aws:ecs:ap-east-2:012345678912:service/managed-instances-cluster/nginx-service-exec-ok |
# | arn:aws:ecs:ap-east-2:012345678912:service/managed-instances-cluster/nginx-service-fargate |
# | arn:aws:ecs:ap-east-2:012345678912:service/managed-instances-cluster/nginx-service |
# +----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------+
bash scripts/check-exec-connect.bash \
--cluster managed-instances-cluster \
--region ap-east-2 \
--service nginx-service
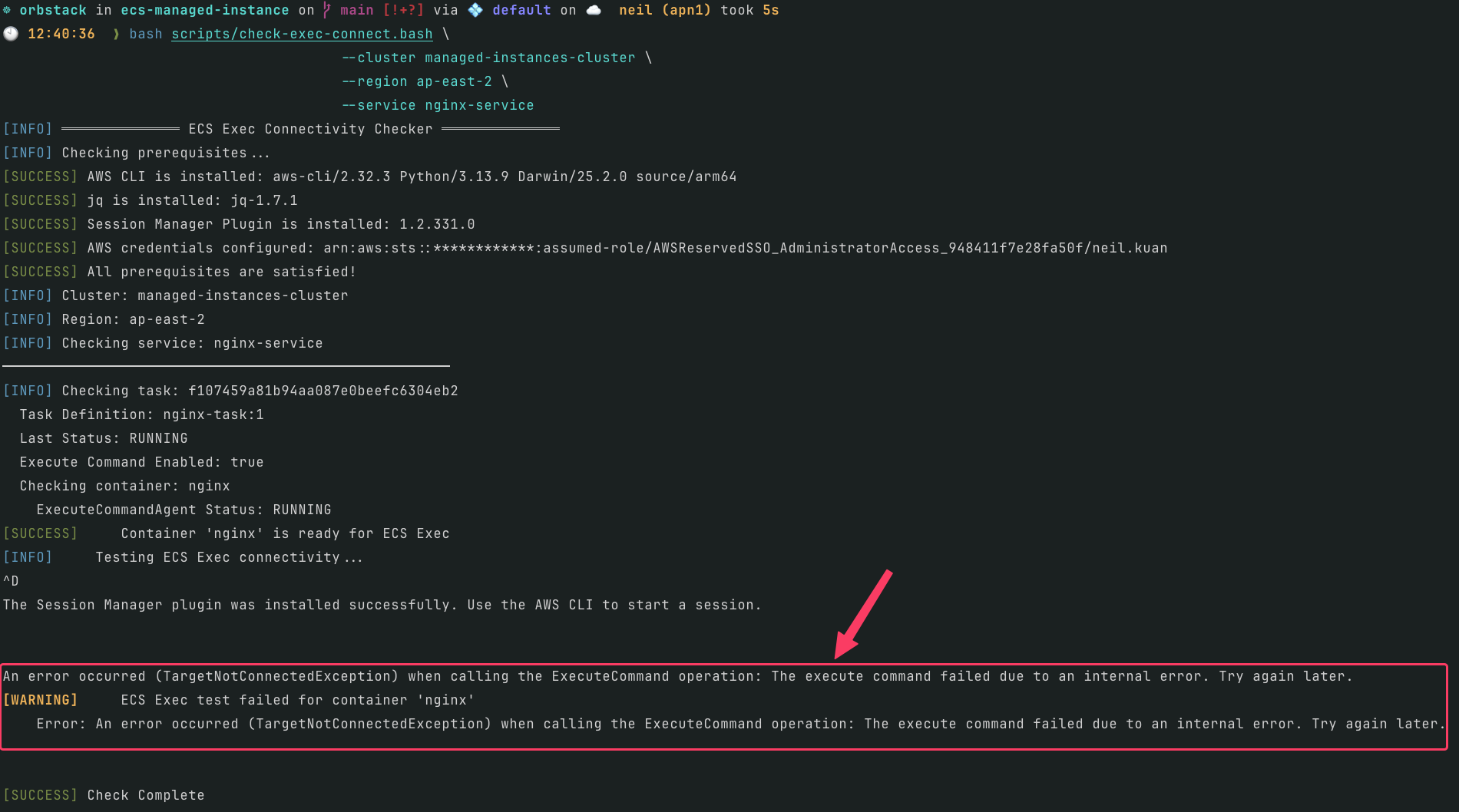
The
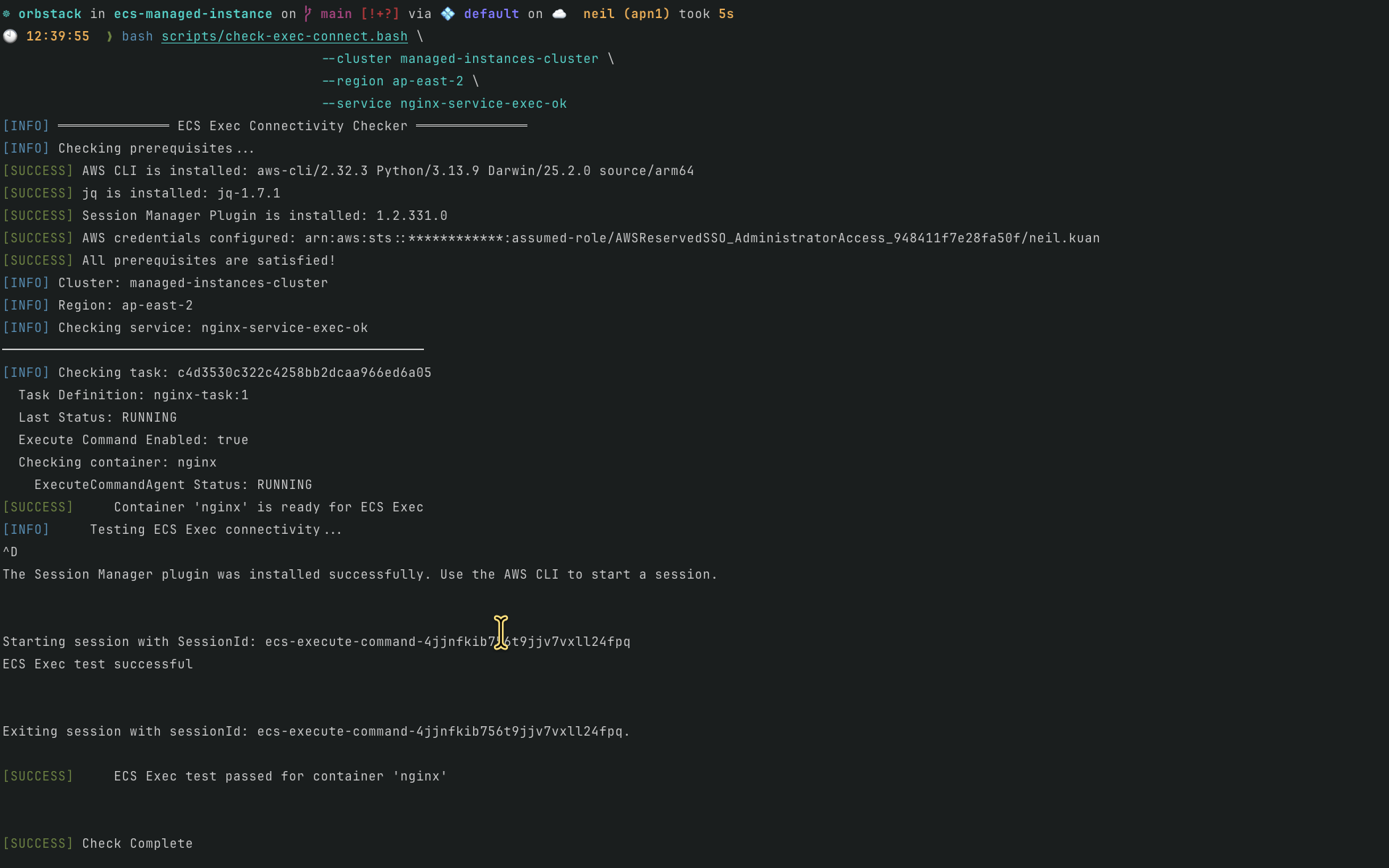
nginx-service-exec-okservice only enables ECS Exec running on Managed Instance.
nginx-service-exec-ok服務僅開啟 ECS Exec,運行於 Managed Instance 上。
Example / 範例:
bash scripts/check-exec-connect.bash \
--cluster managed-instances-cluster \
--region ap-east-2 \
--service nginx-service-exec-ok
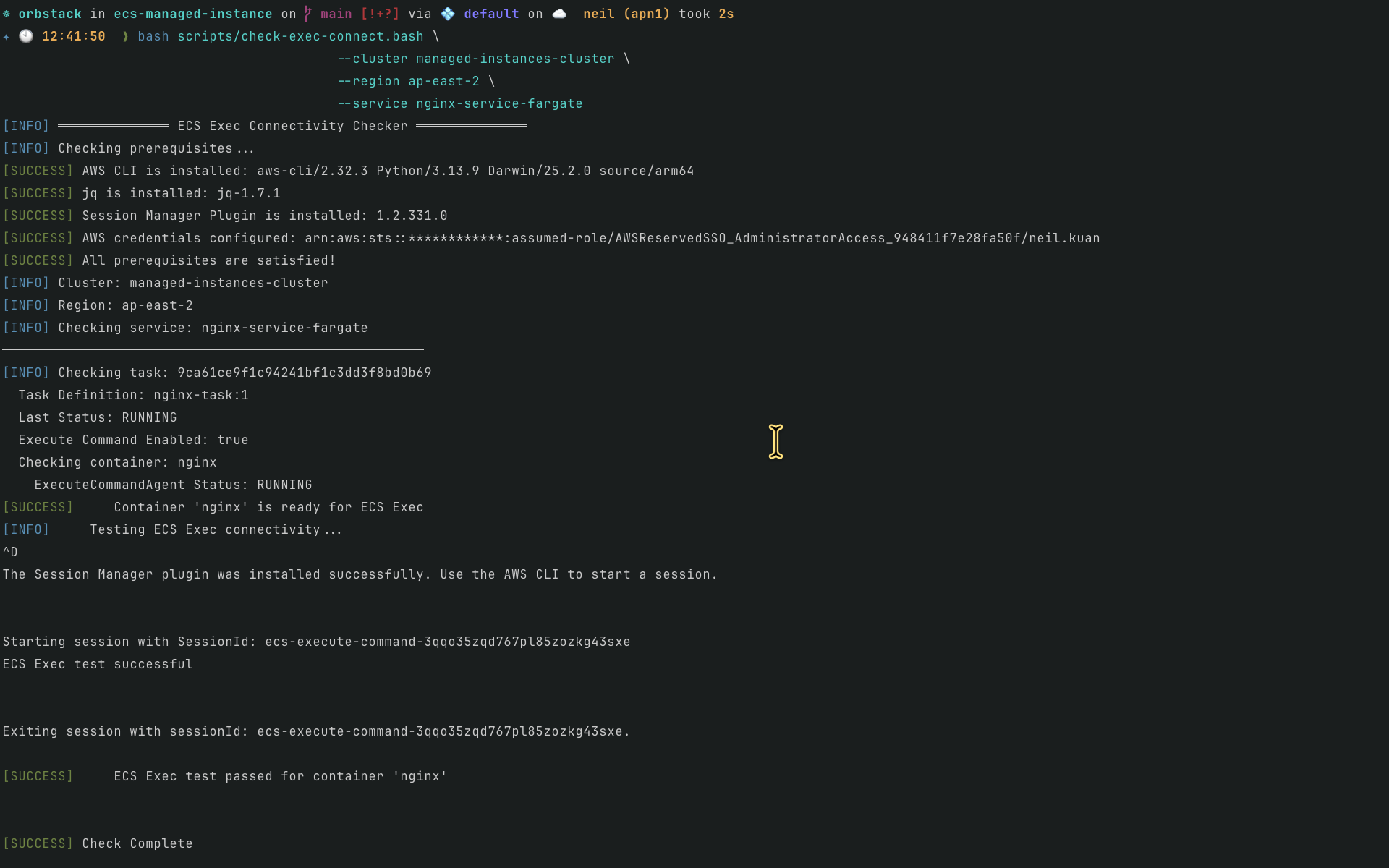
The
nginx-service-fargateservice enables both ECS Service Connect and ECS Exec running on Fargate.
nginx-service-fargate服務同時開啟 ECS Service Connect 以及 ECS Exec,運行於 Fargate 上。
Example / 範例:
bash scripts/check-exec-connect.bash \
--cluster managed-instances-cluster \
--region ap-east-2 \
--service nginx-service-fargate
Summary Table / 總結表格
| Service Name | Launch Type | ECS Service Connect | ECS Exec | Result |
|---|---|---|---|---|
nginx-service |
Managed Instance (EC2) | ✅ Enabled | ✅ Enabled | ❌ Connection Failed |
nginx-service-exec-ok |
Managed Instance (EC2) | ❌ Disabled | ✅ Enabled | ✅ Works |
nginx-service-fargate |
Fargate | ✅ Enabled | ✅ Enabled | ✅ Works |
| 服務名稱 | 啟動類型 | ECS Service Connect | ECS Exec | 結果 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
nginx-service |
Managed Instance (EC2) | ✅ 啟用 | ✅ 啟用 | ❌ 連線失敗 |
nginx-service-exec-ok |
Managed Instance (EC2) | ❌ 停用 | ✅ 啟用 | ✅ 正常 |
nginx-service-fargate |
Fargate | ✅ 啟用 | ✅ 啟用 | ✅ 正常 |
Architecture Diagram / 架構意象圖
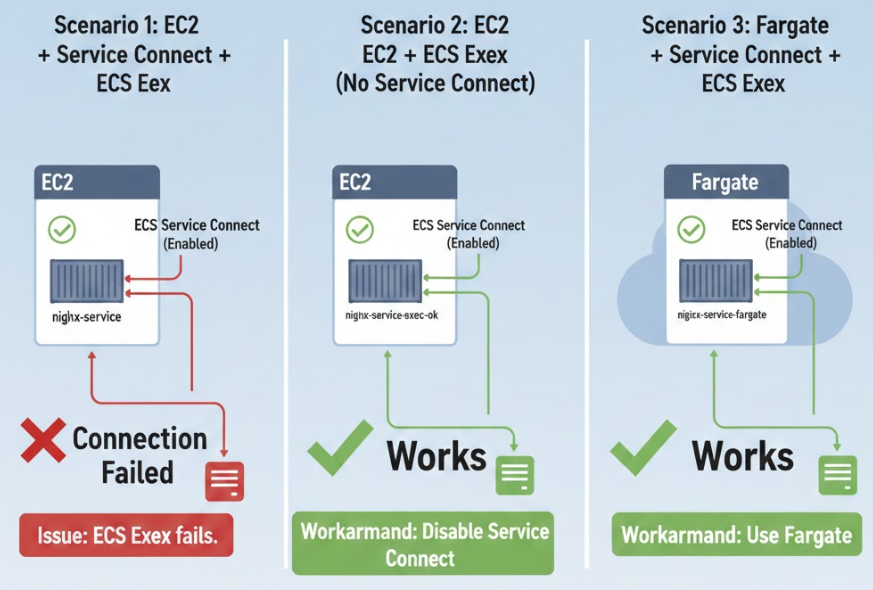
Conclusion / 結論
Issue: When both ECS Service Connect and ECS Exec are enabled on a Managed Instance (EC2), the ECS Exec connection fails.
問題:當 Managed Instance (EC2) 同時啟用 ECS Service Connect 與 ECS Exec 時,ECS Exec 連線會失敗。
Workaround: Either disable ECS Service Connect on Managed Instance, or use Fargate instead.
解決方法:在 Managed Instance 上停用 ECS Service Connect,或改用 Fargate。
